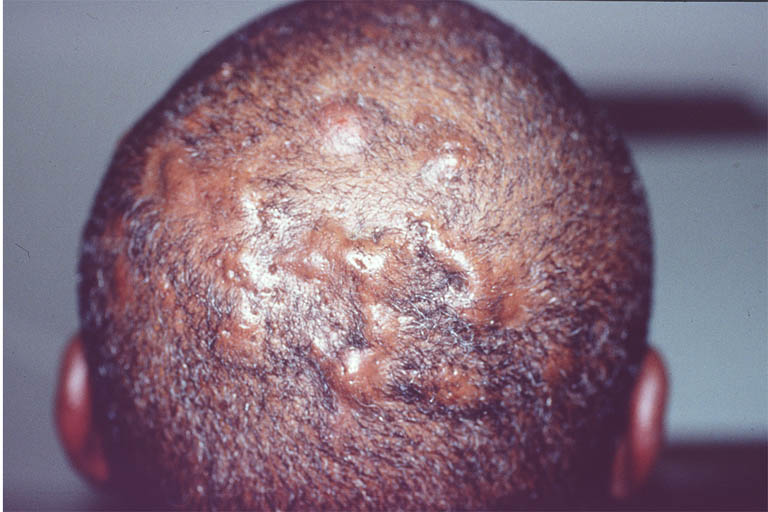
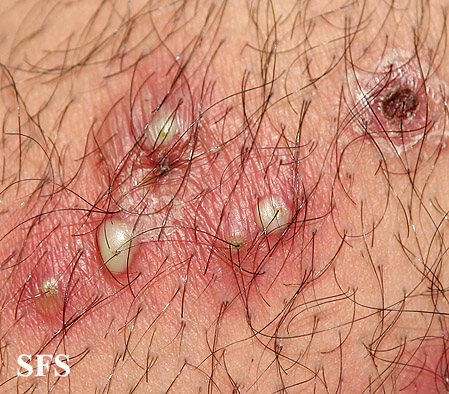
For recurrent uncomplicated superficial folliculitis, use of antibacterial soaps and good hand washing technique may be all that is needed. For refractory or deep lesions that have a suspected infectious etiology, empiric treatment with topical and/or oral antibiotics that cover gram-positive organisms may be of benefit. If a patient does not improve with a standard course of antibiotics, other causes of folliculitis must be investigated.If systemic antibiotics are indicated, coverage should include S aureus, because S aureus is the most common pathogen. This organism often is penicillin resistant; therefore, dicloxacillin or a cephalosporin is the first choice. Methicillin-resistant organisms are becoming more common, and treatment may require clindamycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, minocycline, or linezolid.
Folliculitis Treatment
Folliculitis Treatment
Folliculitis Treatment
Folliculitis Treatment
Folliculitis Treatment
Folliculitis Treatment
Folliculitis Treatment
Folliculitis Treatment
Folliculitis Treatment
Folliculitis Treatment







No comments:
Post a Comment